Catalysis
Catalysis enables the synthesis of molecules, providing commercial and environmental benefits by:
- Providing selectivity when a chemical reaction has one or more potential reaction pathway.
- Enabling shorter and more material efficient chemical processes.
- Increasing the rate of a chemical reaction by lowering the activation energy of a reaction.
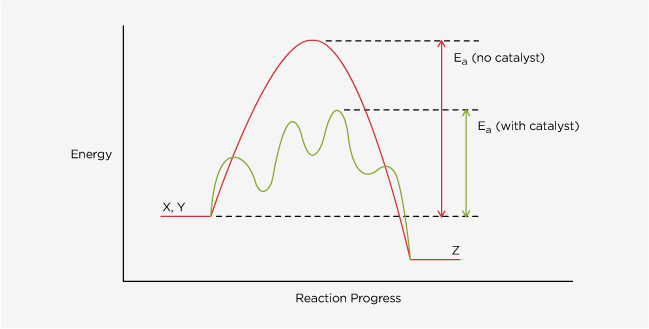
A catalyst should be returned unchanged after the chemical reaction. The catalyst generally works by either changing the structure of a molecule or by bonding to reactant molecules causing them to combine, react, and release a product.
The production of the vast majority of industrially important chemicals, be it in the field of pharmaceutical, agricultural, polymer, speciality or bulk chemicals, involves catalysis at some stage of the manufacturing process.